Essential Hydration Guidelines for the Elderly
It’s essential for everyone to maintain proper hydration, but this need becomes even more critical as we age. Dehydration in older adults can result in a variety of health complications. This article discusses the optimal water intake for seniors and offers comprehensive guidelines to ensure they maintain adequate hydration levels.
As we grow older, our body’s water content diminishes, and our sense of thirst weakens. This combination significantly increases the risk of dehydration. Maintaining adequate hydration is important for several reasons:
- Temperature Regulation: Water helps keep body temperature consistent
- Joint Lubrication: Adequate hydration keeps joints healthy and flexible.
- Cell Function: Every cell in the body requires water to function properly.
- Preventing Constipation: Sufficient fluid intake helps maintain bowel regularity.
Understanding Dehydration Types
Dehydration happens when the body expels more fluids than it absorbs, resulting in an inadequate water level for normal bodily operations. There are three primary forms of dehydration:
- Isotonic Dehydration: This is the most common form, where there is an equal loss of water and electrolytes. It often results from conditions like diarrhea or vomiting.
- Hypertonic Dehydration: In this type, the body loses more water than electrolytes. It can occur due to prolonged fever, excessive sweating, or insufficient fluid intake, leading to increased sodium levels in the blood.
- Hypotonic Dehydration: Here, the body loses more electrolytes than water. This can happen with chronic illnesses, certain medications, or excessive fluid intake without enough electrolytes, causing a drop in sodium levels.
Understanding these types can help in diagnosing and treating dehydration effectively.

Dehydration in Older Adults: Stages and Symptoms
Older adults typically experience hypertonic dehydration, which should be a cause for concern. Initially, water-electrolyte imbalance occurs asymptomatically, and numerous symptoms appear only after some time.
Stage 1:Dehydration manifests with a loss of 2-4% of total body weight. Older adults experience intense thirst, dry mouth, weakness, drowsiness, and nausea. Additionally, they may suffer from bloating, headaches, dizziness, loss of appetite, hypotension, vision or speech disturbances, and muscle cramps.
Stage 2:Dehydration progresses with a loss of 5-6% of body weight, accompanied by drowsiness, tingling, numbness, and irritability
Stage 3:This stage is particularly dangerous for health. A water loss of 10-15% of body weight can lead to seizures, impaired consciousness, and loss of speech and consciousness.
Frequency of Health Problems in Older Adults Due to Dehydration
Fluid deficiency in the body occurs much more frequently than it is recognized. Symptoms indicating dehydration include decreased skin elasticity, dizziness, headache, low blood pressure, cracked lips, constipation, and urinary tract infections.
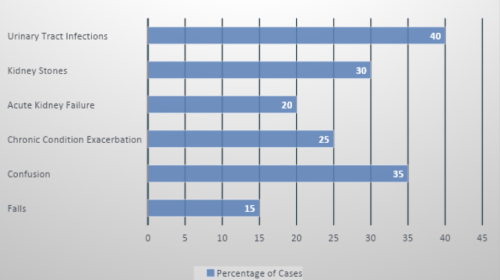
The graph above illustrates the frequency of various health problems in older adults due to dehydration. It highlights the significant impact of dehydration on health, showing that urinary tract infections (40%) and confusion (35%) are among the most common issues, followed by chronic condition exacerbation (25%), kidney stones (30%), acute kidney failure (20%), and falls (15%).
Key Takeaways:
Fluid deficiency in the body occurs much more frequently than it is recognized. Symptoms indicating dehydration include decreased skin elasticity, dizziness, headache, low blood pressure, cracked lips, constipation, and urinary tract infections.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): The most frequent problem, occurring in 40% of cases, dehydration often leads to a higher concentration of urine, which can cause infections.
- Confusion: Dehydration can affect cognitive function, leading to confusion in 35% of older adults.
- Kidney Stones: In 30% of cases, dehydration results in kidney stones due to reduced urine volume, which allows stone-forming substances to crystallize.
- Chronic Condition Exacerbation: Conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases can worsen with dehydration, affecting 25% of individuals.
- Acute Kidney Failure: Occurs in 20% of cases due to the kidneys’ inability to filter waste effectively when dehydrated.
- Falls: Dehydration can lead to dizziness and weakness, resulting in falls in 15% of older adults.
Ensuring adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining health and preventing these problems among older adults.
Daily Water Intake Recommendations
The general guideline for adults is to drink approximately 8 glasses (64 ounces) of water daily. However, for elderly individuals, this recommendation may need to be adjusted based on various factors, including health conditions, medications, and activity levels.
How Much Water Should Seniors Drink?
Most seniors should aim to drink at least 6-8 cups (1.5-2 liters) of water daily. Hydration can come from a variety of sources, including juices, milk, soups, and even certain foods. It’s important to be mindful of caffeinated beverages, as they can have a diuretic effect and should be consumed in moderation.
Specific Recommendations Based on Age and Gender
- For a 65-Year-Old Woman: Aiming for about 8 glasses of water daily is recommended, though this can vary based on her activity level and overall health.
- For an 80-Year-Old Woman: She should also target around 8 glasses of water per day. However, adjustments may be necessary if she has health conditions such as kidney issues.
- For a 90-Year-Old Individual: It is advisable to strive for at least 6-8 glasses of water daily. Consulting with a healthcare provider is important to personalize hydration needs.
Practical Tips for Ensuring Adequate Hydration
- Set a Schedule: Encourage regular drinking throughout the day instead of waiting until feeling thirsty.
- Use Reminders: Utilize alarms or smartphone apps to remind seniors to drink water.
- Offer a Variety: Provide different types of fluids to make drinking more enjoyable.
- Monitor Urine Color: Light-colored urine usually indicates proper hydration, while dark urine suggests a need for more fluids.
Ensuring the Well-being of Seniors with Angel Care Inc. – Home Care Agency NY
Maintaining proper hydration is essential for the overall health and well-being of elderly individuals. Understanding how much water seniors should drink and implementing practical strategies to encourage regular fluid intake can help prevent dehydration and its associated health risks.
Caregivers and seniors can work together to promote adequate hydration. For personalized advice, seniors should always consult with their healthcare providers to determine the optimal amount of fluids based on their unique health needs.
For more information on caring for seniors and ensuring their well-being, visit our Home Care Agency NY website. Our team is dedicated to providing comprehensive care and support to help elderly individuals lead healthy and fulfilling lives.

Veterans' spouses play a vital role in providing care and support to their partners. To help them navigate their lives and foster both their personal and professional growth, a variety of benefits for spouses of disabled veterans have been designed in recognition of their immense contributions. The following is a detailed look at the benefits available to spouses of disabled veterans, particularly those with a 100% disability rating. VA Assistance Programs for Spouses of Disabled Veterans To be eligible for VA assistance programs for spouse of 100 disabled veteran ratings, the spouse must be legally married to the veteran. Additionally, the disability rating must be determined by the Department of Veterans Affairs, and the disability must be service-connected. An eligible survivor of a service member who dies during active duty or from a service-connected disability can receive Dependency and Indemnity Compensation (DIC). Pension for surviving spouses of deceased wartime veterans who are low-income and unmarried. In the CHAMPVA program, eligible veterans receive health care benefits that cover most medical services and supplies. Learning Support for Partners of Injured Military Service Members Fry Grant: Offers learning advantages to the kids and widows/widowers of military personnel who passed away while serving. This encompasses payment for schooling, a regular allowance for housing, and a bonus for educational materials and necessities. Program for the Education of Dependents of Veterans (DEA): Provides up to three years of educational and training support to dependents of veterans who are permanently disabled because of a condition related to their service. This support is available for both college and certificate courses, apprenticeships, and training while working. Job Guidance: Offered by the VA, job guidance assists partners in examining different job options and making educated choices regarding their learning and work objectives. Rental and Mortgage Help VA-Guaranteed Mortgage for Spouses: Partners of veterans who have passed away while serving or due to a disability related to their service might be eligible for a VA-backed mortgage. This can lead to better loan conditions and sometimes even remove the requirement for a down payment. Specialized Housing Assistance (SHA) Program: Helps veterans with certain disabilities related to their service get funding or make changes to their homes to suit their requirements. Spouses of veterans who are still alive and receiving this support can remain eligible. Holistic Support Comprehensive Assistance: The VA offers a range of support services, including therapy to assist partners in dealing with the difficulties of their loved one's disability, such as support for mental health, guidance for marriage and family issues, and tools for managing stress. Temporary Relief for Caregivers: Provides a brief break for caregivers by offering short-term care for the disabled veteran, giving the spouse an opportunity to relax and rejuvenate. In-Home Assistance for Veterans: Vital Details for Service Members' Families A lot of military households might not know about the home health care services that are out there for veterans. If you or someone close to you is looking after a veteran, here's a guide on how to find and take advantage of these services. Offerings: In-Home Nursing Care, Break Care, Assistance with Daily Living, and In-Home Health Care Assistance In-Home Care Nursing (Extended Support): Offers skilled nursing services around the clock for individuals requiring advanced medical care, including support for feeding tubes, tracheostomies, breathing machines, and intravenous lines. Individuals Providing Home Care and In-Home Care Assistants: Help older or disabled veterans with their everyday tasks, aiding them to remain in their homes for as long as feasible. They support with activities such as eating, getting dressed, personal hygiene, bathing, minor cleaning, washing clothes, and purchasing groceries, all while being overseen by a Registered Nurse. Temporary Care: Offers brief care services to give a break to main caregivers, usually for durations ranging from a few hours to a day. Home Care Angel Care Ink. Support Veterans The wide range of support offered to partners of disabled veterans covers many areas of life, such as financial aid, learning opportunities, medical services, and job-related help. Through these supports, partners can improve their standard of living, seek out educational and job chances, and get the help they need to properly support their disabled veteran spouse. Knowing and getting this support can greatly affect the lives of those who have given so much for their nation. At Angel Care, we offer help with everyday activities and additional requirements in in-home care.

In the realm of home care, making the right choice for yourself or a loved one can be a daunting task. With options like the Consumer Directed Personal Assistance Program (CDPAP) and traditional home care, understanding the nuances of each is crucial. This article aims to dissect the differences between CDPAP and traditional home care, weigh the pros and cons of each, and offer guidance on how to make an informed decision based on individual needs. Additionally, we will explore how CDPAP is reshaping the home care industry. Understanding the Differences Between CDPAP and Traditional Home Care At its core, the distinction between CDPAP and traditional home care lies in the level of control and flexibility offered to the care recipient. Traditional Home Care: This model involves receiving care from professional caregivers employed by a home care agency. These caregivers are typically licensed and trained to provide a range of services, from personal care to medical assistance, depending on their qualifications. CDPAP: This New York State Medicaid program allows care recipients to hire, train, and direct their own caregivers. Interestingly, the caregivers can be family members or friends, excluding spouses or designated representatives. This model emphasizes a personalized, consumer-directed approach to care. Pros and Cons of CDPAP Pros: Personalization and Comfort: With CDPAP, care recipients can choose caregivers they trust and are comfortable with, enhancing the personalization and comfort level of the care provided. Flexibility: CDPAP offers more flexibility in terms of scheduling and services. Caregivers can perform a wide range of tasks, including nursing and medical tasks, after appropriate training. Empowerment: It empowers individuals by giving them direct control over their care, leading to potentially higher satisfaction. Cons: Administrative Responsibilities: The care recipient or their representative must manage payroll, tax, and other administrative tasks. Limited Availability: CDPAP is a Medicaid program and is not available to those not eligible for Medicaid. Also, it's specific to certain states, like New York. Pros and Cons of Traditional Home Care Pros: Professionalism and Training: Caregivers are professionally trained and licensed, ensuring a high standard of care. Less Administrative Burden: The home care agency handles all administrative tasks, including payroll, taxes, and scheduling. Backup Care: Agencies typically offer backup caregivers in case the primary caregiver is unavailable. Cons: Less Personal Control: Care recipients have limited say in choosing their caregiver and scheduling their hours. Cost: It can be more expensive than CDPAP, especially if not covered by insurance or Medicaid. How to Choose Between CDPAP and Traditional Home Care Choosing between CDPAP and traditional home care depends on individual circumstances, including medical needs, personal preferences, and financial considerations. Here are some factors to consider: Level of Comfort and Trust: Do you prefer a caregiver who is a family member or friend, or a professional from an agency? Willingness to Manage Administrative Tasks: Are you or a family member willing and able to handle the administrative responsibilities that come with CDPAP? Financial Considerations: Assess the costs and your eligibility for Medicaid or other insurance coverages. How the CDPAP is Impacting the Home Care Industry CDPAP is significantly impacting the home care industry by introducing a consumer-directed approach. It's compelling traditional agencies to reconsider their models and adapt to a landscape where personalization and consumer control are increasingly valued. The program is also highlighting the importance of flexible, tailored care plans that meet the unique needs of each individual. Choose your in-home care with Angel Care ink. Deciding between CDPAP and traditional home care is a deeply personal choice that hinges on specific needs, preferences, and circumstances. By understanding the pros and cons of each, assessing your personal situation, and considering the evolving landscape of the home care industry, you can make a decision that best supports your or your loved one's health, well-being, and independence. No matter what you choose for yourself or your loved one, finding a trusted home care agency that truly cares about its patients is crucial. Angel Care Inc. is here for you. Start your new life with us today. Contact our manager to learn more about your opportunities.



